As technology continues to grow exponentially, we are finding more ways to incorporate them into helping society improve. An example of this that I wanted to delve into is the use of therapeutic robots, specifically for patients with dementia. There have been several types of these robots on the market that can track, bond, and administer data about a patient instead of having a 24/7 caretaker in the home. The robots are able to talk with the patient, tell them when to take their medicine, and document anything that happens. The information is then relayed onto a server, in which the customer has no access to. The security threats for this technology are very in depth and cumbersome. It is scary to know that all of your data is located in a place where you have to access to. The server has unique data such as medical history, daily activities, and records anything you say while the robot is in action and functioning. According to studied, the robots help reduce depression in patients and boost self esteem. They act as a pet who does not need to be fed or taken care of.
Even if these robots can be very helpful in improving the lives of elderly people with mental conditions, the security threats are very evident and terrifying. Anyone can hack into a database and recall any unique information and data that is held in the tables. It is even more scary because the customers have no access to the database and they do not know what exactly is being stored about them.
Questions:
1. Is the use of these robots worth the security threats that are posed?
2. Could this technology be further used maybe in children with cognitive disorders such as Autism or even something more serious like Schizophrenia?
3. Do you think the customers should be able to access the database and see the exact data and information that is being held about them?
This is a link to an interesting YouTube video that shows how it works:
Click Here to View! - link broken. Search "pets and dementia" for many examples.
Original article:
Dementia Care Gets Innovative
Sunday, April 21, 2019
Thursday, April 18, 2019
Blockchain and its Implications on Real Estate
In an ever-developing world that is constantly changing and evolving in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, some industries still lag behind in their innovation. One of these industries is real estate, as realtors, brokers, and title agencies all continue their operations today largely as they have for the past few decades. However, Blockchain technologies are one source of disruption that may finally force real estate as an industry to adapt to the times.
Currently, one area within real estate that is especially liable to be disrupted is titling. The de facto method for changing the legal possession status of properties is for a buyer or seller of a home to go down to the local courthouse, sift through binders of deeds that are feet thick and have records dating back decades, and once the deed is found physically erase the previous owner and replace their name with the new owner. This is very inefficient for a multitude of reasons. Although this process could be digitalized in a variety of ways, many companies are actively striving towards a blockchain based solution.
In multiple countries abroad including Sweden, as well as Vermont and Wyoming here in the United States, local, county and state governments are exploring the possibility of using public blockchain ledgers to host title records. Essentially, once these title records are uploaded to the blockchain any person interested in finding title and property records will be able to do so instantaneously by combing through the blockchain, This solution will eliminate the need for the endless stream of paper documents that are still in use despite being outdated for years.
Given that real estate is an industry which will never disappear because of the universal need for housing and safety, the implications of this blockchain disruption will be widespread. There is a possibility that real estate agents may be eliminated altogether if the entire home sale transaction process can be placed on the blockchain. Furthermore, countless other jobs that were previously human facing and based entirely upon person to person interaction may be eliminated. The relationship between Blockchain and its increasing and imminent presence in the real estate industry is an extremely interesting example of how even the industries most resistant to technological integration are beginning to change. Only time will tell exactly how this will affect our society, but it is certain that many lives will be altered forever.
Questions to ponder:
1. At what point does technical innovation do more harm to peoples' lives compared to the value it creates?
2. What other industries are like real estate in that they are heavily resistant to change and technology?
3. Is Blockchain technology really the next big thing that will change our world, or is it simply another step towards what comes next?
Currently, one area within real estate that is especially liable to be disrupted is titling. The de facto method for changing the legal possession status of properties is for a buyer or seller of a home to go down to the local courthouse, sift through binders of deeds that are feet thick and have records dating back decades, and once the deed is found physically erase the previous owner and replace their name with the new owner. This is very inefficient for a multitude of reasons. Although this process could be digitalized in a variety of ways, many companies are actively striving towards a blockchain based solution.
In multiple countries abroad including Sweden, as well as Vermont and Wyoming here in the United States, local, county and state governments are exploring the possibility of using public blockchain ledgers to host title records. Essentially, once these title records are uploaded to the blockchain any person interested in finding title and property records will be able to do so instantaneously by combing through the blockchain, This solution will eliminate the need for the endless stream of paper documents that are still in use despite being outdated for years.
Given that real estate is an industry which will never disappear because of the universal need for housing and safety, the implications of this blockchain disruption will be widespread. There is a possibility that real estate agents may be eliminated altogether if the entire home sale transaction process can be placed on the blockchain. Furthermore, countless other jobs that were previously human facing and based entirely upon person to person interaction may be eliminated. The relationship between Blockchain and its increasing and imminent presence in the real estate industry is an extremely interesting example of how even the industries most resistant to technological integration are beginning to change. Only time will tell exactly how this will affect our society, but it is certain that many lives will be altered forever.
Questions to ponder:
1. At what point does technical innovation do more harm to peoples' lives compared to the value it creates?
2. What other industries are like real estate in that they are heavily resistant to change and technology?
3. Is Blockchain technology really the next big thing that will change our world, or is it simply another step towards what comes next?
8 Major Companies Using Drone Technology
As we know the world of technology is changing all around us
and we are coming up with new ways to do jobs that we have never thought of.
One way we are doing our jobs differently is through the use of drones. There
are many companies that have been using drones to get their jobs and processes
done more efficiently. I will touch one
a few companies that are using drones to there advantage.
There are some of the industries leading companies that are
using drones. One major company that is using drones is Shell Oil Company. It
seems a little weird that a oil company could put drones to use but they do.
Shell uses the help of drones to inspect their refineries and make sure that
everything is meeting the standards that they need to meet. Many times inspections
can be dangerous because of the area that one might have to travel to or the
fumes and toxins one might be exposed to. With the use of drones Shell does not
have to expose their employees to these dangerous situations.
Another major player in the drone field is of course Amazon.
Amazon seems to be the leading company when it comes to new technology
integration. Amazon is looking at the use of drones for Prime Air delivery,
this is a service in which the time between placing the order and receiving the
order is only about half an hour. This would greatly increase Amazons customer
satisfaction and launch them past there competitors.
Lastly, the DHL Corporation is another key player in using
the technology of drones to make their processes and delivery better. The DHL Corporation
delivers blood and pharmaceutical supplies and drugs to remote locations that
are hard to get to. With the use of drones DHL can deliver these supplies
quicker and easier. This will help them in savings many lives that could be lost
due to the remote location of where they are being taken care of. This is huge
in the health industry and great for everyone involved.
Questions:
1.
Do you think that the use of drones is a good
idea? Why or Why not?
2.
What are some other ways that you could see
drones being helpful in making companies better and more competitive?
3.
What do
you think is the next big thing that drones will be used for?
Tuesday, April 16, 2019
Going Green Goes Wrong...
Lyft which is the top transportation service in the United States has recently been making a few changes in their app in efforts to go “Green.” For example, they launched a new feature which allows users to share a ride with user who are in the same area or going to a near destination. In another attempt, Lyft decided to acquire the Motivate company which a bikeshare operator.
Lyft’s goal is to reduce the need of using personal cars and provide affordable and reliable ways to get around town. The company has also expanded to carpooling and scooter renting. The problem is that Lyft has been receiving complaints from electric bicycle users that have said that the braking force in the front wheel is very strong. As a result Lyft has removed the electric bicycles in New York, Washington DC and San Francisco.
While the company is hard at work trying to resolve the issue they have made non-electric bicycles available to users as an alternative. This was a very interesting topic to me because I feel like many companies are trying hard to incorporate technology as a way of being environmentally friendly but it also comes with many risks. The main question that this concept arises is if environmentally friendly solutions which are technology based really worth the risks? There are many other non-technological solutions to reducing car usage that are also much more simple, but then also the benefits of technology based solutions like getting to your destination in half the time and effort will be lost. How can we meet a middle ground?
Link to articles: Lyft Pulls Electric Bycicles, Lyft Acquires Bike Company
Google Photos Services Security
The usage of Google Photos is very
popular. “It reached 100 million
users after five months, 200
million after one year, and 500 million as of May 2017, with Google announcing that
over 1.2 billion photos
are uploaded to the service every day, with the grand total of all uploaded
content measuring over 13.7 petabytes of storage. “
It has
recently been discovered that Google Photos has possible security vulnerabilities
addressing user’s private data. After recent exposure of a malicious threat to
the Google Photos services showed that hackers had the access to the
geo-locations of the pictures saved to the servers; researchers name this a
browser side-channel leak.
Also, YouTuber
Devon Crawford recently released a video about what he found when he downloaded
his private Google data. As he was going through his data he found that Google
Photos stores all your information and pictures publicly. Even videos and
photos that he did not post onto any social media or backed up in Google Photos
were stored in public URLs. This was particularly alarming because many people believe
that the information stored on their device is private. These URLs even stored
pictures and videos that had been deleted from his end of the app. He also found that Google has been storing
information about his actions on other sites like amazon.
It is
important to understand that Google is primarily an ad company rather than a
search company. The sell the extensive data that they collect about their users
to broker ad sales. Many call this “surveillance capitalism” because tracking
is essential to their business. So much so that in 2018 about 86% of their revenue
came from their ad business. So, Google services profit from connecting your
online persona to your offline persona.
For more
information check out the articles and video:
Questions
to consider:
1. If the public
became aware of the extent that Google services record their digital data, how
would they react?
2. Is it ethical
for Google services to keep such an extensive record of our information?
3. Why would
Google services store user’s personal information in public links?
Monday, April 15, 2019
German Automaker Mercedes Benz incorporates Blockchain into their Supply Chain!
In a press release published at the end of February Mercedes-Benz announced that the company had developed a platform based on blockchain technology to increase transparency and sustainability in complex supply chains.
Mercedes has decided to partner with Icertis a software company based in the United States in the expansion of the blockchain technology for supply chain usage. The two companies have passed the prototype phase which gives Mercedes the ability to store documents and contracts in intricate supply chains. Currently, the two firms are in the testing phase of the pilot project. This phase allows for the formation of a transparent and workable mapping of organized documents across the whole supply chain.
With other German automobile manufacturers such as Porsche increasing funding towards blockchain initiatives. It is important to note that “Blockchain technology has the potential to fundamentally revolutionize our procurement processes [...] With our Blockchain-prototype, we are in the first step testing one of diverse possible applications with the aim of increasing transparency beyond our direct suppliers” said Wilko Stark a member of the Mercedes – Benz divisional board.
For more information Check Out the Article:https://cointelegraph.com/news/mercedes-benz-to-use-blockchain-tech-for-sustainable-transaction-book-supply-chains
Questions to Consider:
Do you think American Car Manufactures will enter the Blockchain space?
What value if any do you think this brings to Mercedes and its suppliers?
If you were the executive of the big three American Car Manufactures such as Ford, GM, Chrysler would you implement Blockchain?
Sunday, April 14, 2019
The Future of Our Roads
One of the greatest technological revolutions of our time may be fast approaching, and has the potential to completely upturn the transportation industry in a way not seen since the advent of the 'horseless carriage'. With the advent and slow-but-steady progress on driverless vehicles of all types, from massive cargo and shipping trucks able to deliver goods across country pausing only to recharge their batteries, to personal taxi services which may eliminate personal vehicle ownership, the future of our roadways looks strikingly different than that seen today. However, this progress doesn't come without great debate: everything from legality and legislation to questions of moral philosophy have been raised.
With LYFTs initial public offering having arrived at the end of march, it's clear that the concept of driverless vehicles isn't merely a technological fad - as part of an industry now worth billions, these companies such as Lyft and Uber have major stakes in pushing for the continued progress towards (and full legalization) of driverless vehicles. Having the ability to command a fleet of "robocars to navigate city streets alone so they can offer rides 24-7 without having human drivers share their takings"is a key part of these ride-sharing companies' business strategies, but many are increasingly concerned with the safety of passengers and other travelers. Legislation is struggling to keep up with the rapid development of technology, and initial testing has received some setbacks, even among its customers. Regarding a Phoenix-based test, “Almost 40 percent of Waymo’s customers registered complaints in reviews seen by the publication, from wrong turns to near-crashes". However, some of these companies argue that their cars still produce less accidents/crashes than an average driver does, and as such continue to push for accelerated testing and lax laws surrounding it.
Considering these facts, I think a few important questions are raised:
- If, in the future, the technology is capable of producing less accidents than a human driver, couldn't the argument be made that it would be unethical to not allow these cars on the road in order to replace human drivers, thus lowering the number of overall collisions?
- In your opinion, how should laws be crafted regarding who is at-fault if harm comes to the passenger even if the 'robocar' is not at fault? Would the company have a responsibility to insure its passengers, or would it still fall to the at-fault driver of the other vehicle?
- Should these companies be allowed to go forward with accelerated testing, even if it bears an increased risk to the public for the sake of more rapid development to hopefully lower traffic collisions and congestion in the future? Is there a hard-line to be drawn at some point (and if so, what might that point be)?
With LYFTs initial public offering having arrived at the end of march, it's clear that the concept of driverless vehicles isn't merely a technological fad - as part of an industry now worth billions, these companies such as Lyft and Uber have major stakes in pushing for the continued progress towards (and full legalization) of driverless vehicles. Having the ability to command a fleet of "robocars to navigate city streets alone so they can offer rides 24-7 without having human drivers share their takings"is a key part of these ride-sharing companies' business strategies, but many are increasingly concerned with the safety of passengers and other travelers. Legislation is struggling to keep up with the rapid development of technology, and initial testing has received some setbacks, even among its customers. Regarding a Phoenix-based test, “Almost 40 percent of Waymo’s customers registered complaints in reviews seen by the publication, from wrong turns to near-crashes". However, some of these companies argue that their cars still produce less accidents/crashes than an average driver does, and as such continue to push for accelerated testing and lax laws surrounding it.
Considering these facts, I think a few important questions are raised:
- If, in the future, the technology is capable of producing less accidents than a human driver, couldn't the argument be made that it would be unethical to not allow these cars on the road in order to replace human drivers, thus lowering the number of overall collisions?
- In your opinion, how should laws be crafted regarding who is at-fault if harm comes to the passenger even if the 'robocar' is not at fault? Would the company have a responsibility to insure its passengers, or would it still fall to the at-fault driver of the other vehicle?
- Should these companies be allowed to go forward with accelerated testing, even if it bears an increased risk to the public for the sake of more rapid development to hopefully lower traffic collisions and congestion in the future? Is there a hard-line to be drawn at some point (and if so, what might that point be)?
What is Facial Recognition?
From touch screens to fingerprint unlocking capabilities to self-driving cars, technology is slowly but surely taking over our everyday lives. An even more incredible technological phenomenon is the emergence of facial recognition. Facial recognition is a collection of biometric data, analyzed by the user’s facial features and structures, in order to verify or identify an individual. Some may be familiar with the use of facial recognition from the new Apple iPhone, the iPhone X. With this new device, individuals can unlock their phone simply by showing their face to the phone screen. Also, even with older versions of the iPhone, you may notice in your photo album that pictures are grouped based off faces your device has recognized and then categorized. This is also done so by the technology used in facial recognition. Here is a picture that breaks down the steps in facial recognition.

How does it work?
Facial recognition software works by focusing on the nodal points on a person’s face, creating an image out of those points, storing the data collected as a faceprint, and then comparing the faceprint to others and separating them. Nodal points are endpoints used to measure variables on a person’s face, such as the length and width of the lips, the depth of the eye sockets, and the shape of a nose. Once this data is collected, it is stored as a digital image or a faceprint. This faceprint is then used as a base for comparing and identifying who the person is. To learn more about how facial recognition works, please click here.
Where is facial recognition used?
As mentioned before, devices such as our phones, carry some form of facial recognition software. Once a picture is taken on an iPhone, it analyzes the facial features and then stores the data as a collection of individuals on the phone. The new iPhone X has the capabilities to unlock your phone by placing your face in front of the screen. Facial recognition is also used for security and law enforcement purposes. Law enforcement uses facial recognition to identify and apprehend suspects in a crime.
A few drawbacks of facial recognition
Facial recognition software isn't completely perfect. There are many variables that go into identifying a person by their facial features and this leaves room for error. According to the article, What is Facial Recognition?: How computers use face scan technology to identify users, here are some limitations that come with facial recognition.
Poor resolution images and poor lighting can reduce the accuracy of face-scanning results.

How does it work?
Facial recognition software works by focusing on the nodal points on a person’s face, creating an image out of those points, storing the data collected as a faceprint, and then comparing the faceprint to others and separating them. Nodal points are endpoints used to measure variables on a person’s face, such as the length and width of the lips, the depth of the eye sockets, and the shape of a nose. Once this data is collected, it is stored as a digital image or a faceprint. This faceprint is then used as a base for comparing and identifying who the person is. To learn more about how facial recognition works, please click here.
Where is facial recognition used?
As mentioned before, devices such as our phones, carry some form of facial recognition software. Once a picture is taken on an iPhone, it analyzes the facial features and then stores the data as a collection of individuals on the phone. The new iPhone X has the capabilities to unlock your phone by placing your face in front of the screen. Facial recognition is also used for security and law enforcement purposes. Law enforcement uses facial recognition to identify and apprehend suspects in a crime.
A few drawbacks of facial recognition
Facial recognition software isn't completely perfect. There are many variables that go into identifying a person by their facial features and this leaves room for error. According to the article, What is Facial Recognition?: How computers use face scan technology to identify users, here are some limitations that come with facial recognition.
Poor resolution images and poor lighting can reduce the accuracy of face-scanning results.
- Different angles and facial expressions, even a simple smile, can pose challenges for face matching systems.
- Facial recognition loses accuracy when the person is wearing items like glasses, hats, scarves, or hairstyles that cover part of the face. Makeup and facial hair can also pose issues for face detection programs.
- Facial scans don’t necessarily connect with a profile, meaning that a scan of a person’s face may not be useful if there are no photos of them in an accessible database. Without a match, the identity of the person behind the face scan can remain a mystery.
- https://www.eff.org/pages/face-recognition
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hgTBLLMtpUA
- https://www.lifewire.com/how-does-a-computer-recognize-your-face-4154178
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/facial-recognition
- What are some other limitations of facial recognition?
- How can facial recognition be harmful to our society?
- What are some ethical/unethical implications that come with facial recognition?
Big Data and it's predictive power on healthcare
A team in Northeaster University developed a model in which they can analyze flu outbreaks. Using tweeter, this team was able to see what areas and what symptoms were the most common. Over 50 million tweets were used to predict the number of cases. Some other information collected was the areas with the highest density and how contagious it was. This method was used for two flu seasons and was able to track flu cases 6 weeks before other tracking methods(CNN). Some of the advantages of analyzing these data are resource allocation and a better understanding of how to treat the virus (Forbes).
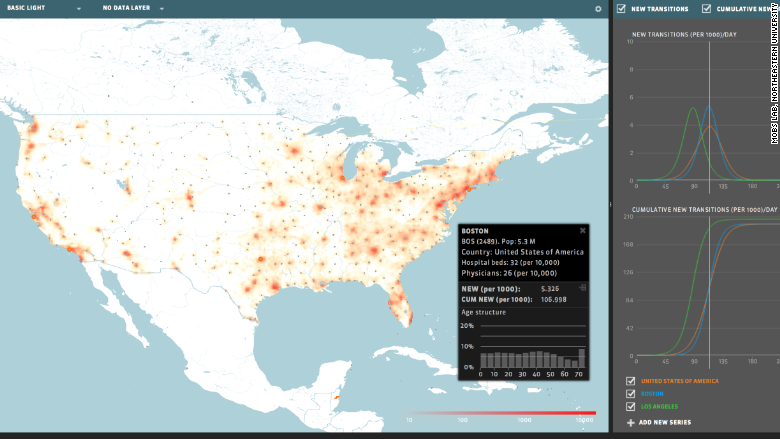

Big Data can tell us a lot about our human behavior, especially that we like to share information. Obviously, not everyone in the US has a twitter account but US Twitter users are a good sample pool to pick on. This sample is so great because is diverse and correlates with the general population. Using this tool will save so many lives and it will help to understand the behavior of diseases.
Do you guys think big data can predict other diseases?
Are we relying too much on big data?
Are there any outliers that can affect this information?
Do you guys think big data can predict other diseases?
Are we relying too much on big data?
Are there any outliers that can affect this information?
Rise of Robotic Process Automation
This Tech Talk
was a combined effort of Brandon Hum and Hannah Miller
With growing technological advances, many
mundane tasks are becoming automated and standardized. There is not a single
industry that is immune to the current technology climate, and thus must adapt
their practices to remain competitive and efficient, much less relevant. The
accounting industry is no exception, as most companies in public accounting
have begun to adopt Robotic Process Automation (RPA) within their routine
practices.
What is RPA?
RPAs are a type of software that allows for
instant processing and analysis of basic or day-to-day transactions. It is
typically a mix with artificial intelligence that allows it to have high-level
thinking at high capacities. It can be programmed to fit different needs
throughout the business, depending on service line, account type, etc. The
trick to RPA is that it requires rule-based processes. When an RPA has defined
boundaries, it can use applications to process information, change data, and communicate with
other systems (Boulton, 2018).
Accounting Application
It is important to note that RPAs are applied
differently depending on the service line. In tax, for example, they have a
base set of rules and different software that would require a different
structure of an RPA. A tax accountant is looking to ensure their client is
meeting regulation and providing proper recording, whereas an auditor is doing
test work to ensure accuracy and proper representation. RPAs are therefore more
suited for audit work because work can be refocused on analysis rather than the
simpler tests required.
In this article by the CPA Journal, they outline three main steps for
the initial use of RPAs.
●
Process Understanding
●
Audit Data Standardization
●
Execution of RPA-based Audit Tests
Process Understanding is the use of RPAs in
the case of repetitive and mundane tasks that do not require high level
thinking nor opinions. In this RPA application, it would be required that the
tasks are extremely broken down as to not confuse the robot. Audit Data
Standardization would have to ensure that data was consistent in terms of its
format so the robot would not have any issues reading or understanding it.
Finally, in Execution of RPA-based Audit Tests, they would potentially need new
software or skills teams that have a higher level of understanding of the new
system.
Current Usage
Big four accounting firm Ernst & Young has been ranked #1 by HFS Research
because of their innovations and implementations of the system. They have been
able to use over 2,000 robots which conduct the work that would equate 2.1
million hours by humans. Currently their focus is developing RPAs for use in
telecom and as an automated process mapping tool (Sankaran and Burgess, 2018).
Pros and Cons
RPAs allow companies to perform tasks at a
much higher rate, driving higher productivity rates. Many bots are fairly
simple to implement, and can be programmed to cover low-value tasks, leaving a
company’s human capital with more time to perform more value-added services to
clients. In an audit firm, many of the data collection and financial sampling
and testing can be handled by a well-programmed bot. This allows auditors to
focus on analyzing and understanding the data to better opine on the financial statements to their client
(Poulikakos & Putnam 2018).
However, RPAs do come with costs. As
automation increases, so does the potential that the company eliminates some of
its human capital. Also, it can be difficult for companies without the
resources or knowledge to properly implement and scale bots to full cover their
needs. A company that tries to program a bot to perform a task without first
investing in the proper IT environment needed will not achieve the success it
intended. Despite this, with a strong plan, a proper IT environment, and the
knowledge base to implement and scale bots between processes, a company can
successfully use RPAs to increase its productivity.
Additional Links
For more information about Robotic Process
Automation, please see the following articles and video.
- Robotic Process Automation: How does it work?
- 7 RPA Training and Certificate Courses
- What is Robotic Process Automation?
4. So You Want to Use RPA
in Audit — Here’s How You Start
Questions
- Do you see
any potential automation within your future career/industry?
- Do you think
there will be any public lashback over the increased use of robots?
Works
Cited
Boulton, C. (2018, September 03). What is RPA? A
revolution in business process automation. Retrieved from https://www.cio.com/article/3236451/what-is-rpa-robotic-process-automation-explained.html
Poulikakos, A. & Putnam, C. (2018, September 19).
Retrieved from https://blog.protiviti.com/2018/09/19/want-use-rpa-audit-heres-start/
Sankaran, A., & Burgess, B. (2018, November 13). EY
ranked #1 in robotic process automation services by HFS Research. Retrieved
from https://www.ey.com/en_gl/news/2018/11/ey-ranked-one-in-robotic-process-automation-services-by-h-f-s-research
Vasarhelyi,
M. A. (2018, July 11). How Robotic Process Automation Is Transforming
Accounting and Auditing. Retrieved from https://www.cpajournal.com/2018/07/02/how-robotic-process-automation-is-transforming-accounting-and-auditing/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)